Thrombectomy Catheter for Treating Stroke Patients with Cerebral Artery Blockage
Center : Neurology Center
Article by : Dr. Chanwit Ankrohwittaya

Patients with symptoms of cerebral artery stenosis and blockage, such as weakness in one side of the body, facial drooping, slurred speech, blurred vision, or imbalance, should seek medical attention within 4.5 hours to receive thrombolytic therapy. This treatment can reduce disability and the risk of death. For patients arriving later or with large cerebral artery blockages, an innovative treatment known as "thrombectomy catheter" or clot retrieval, along with the Biplane DSA machine, can effectively and safely remove the blood clot.
Contents
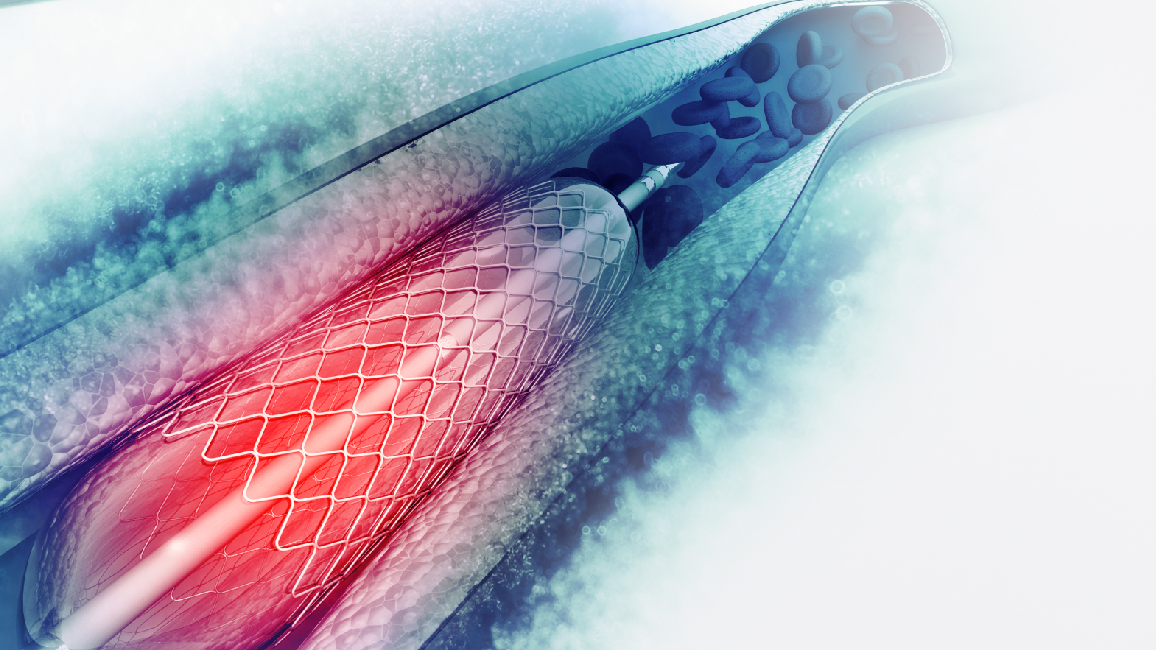
Thrombectomy Catheter (Clot Retrieval)
Thrombectomy catheter treatment involves inserting a catheter through a large artery in the groin to the blockage site and removing the blood clot to reopen the artery without major surgery. This allows blood to flow to the brain again, promoting recovery. It is suitable for patients with large blood clots unresponsive to thrombolytics or those arriving after the 4.5-hour window, extending treatment time to up to 6 hours, or 24 hours in some cases.
This method has an 80% success rate in reopening blocked arteries, reducing complications, and lowering the risk of paralysis. Patients generally respond well and show significant improvement.
When to Use Thrombectomy Catheter
Thrombectomy catheter treatment is suitable for patients who:
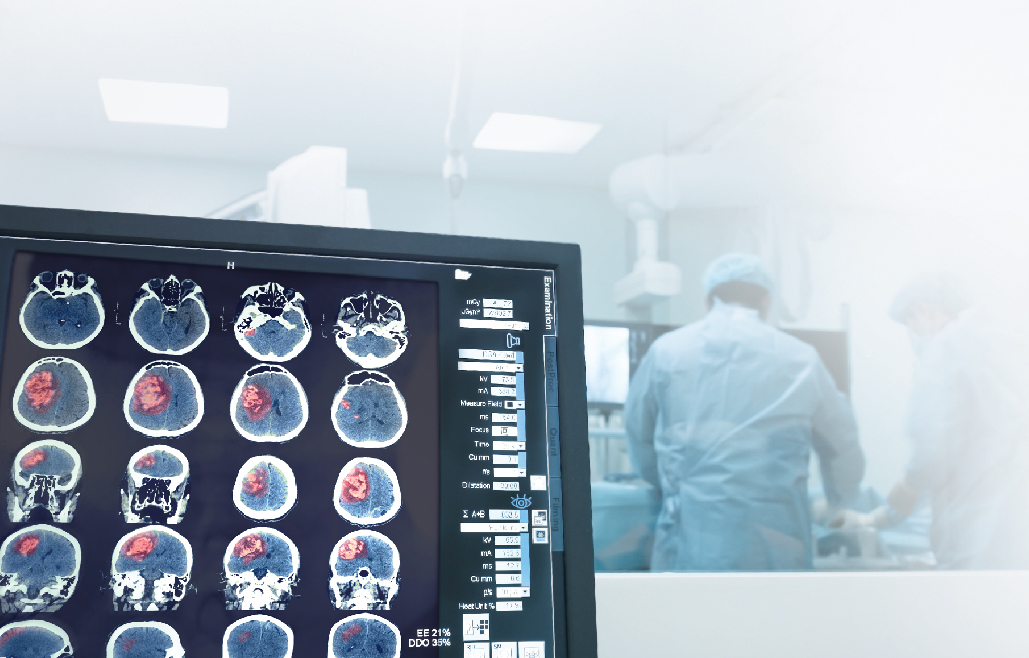
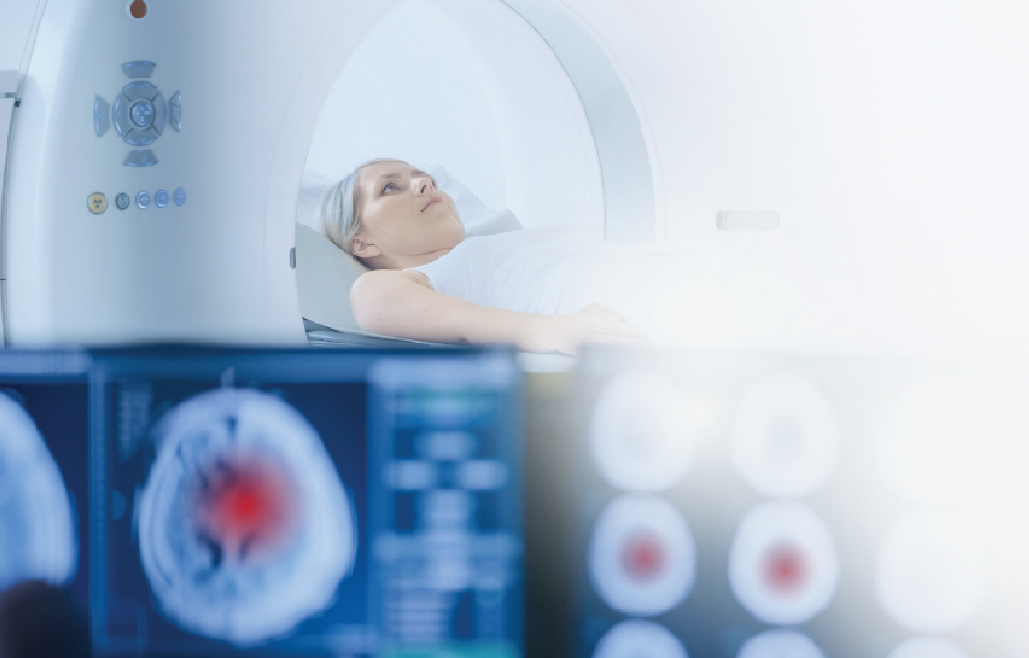
- Arrive at the hospital after the 4.5-hour window for thrombolytic therapy and have a large cerebral artery blockage detected by CT or MRI, still within treatable conditions.
- Did not respond to intravenous thrombolytic therapy or continue to show abnormal symptoms, provided the blockage is in a large cerebral artery. This method is also considered for patients who have contraindications for thrombolytics or have abnormal blood clotting conditions.
Procedure Steps:
- Administer anesthesia.
- Clean the groin area.
- Make a small incision for catheter insertion.
- Insert the catheter through the large groin artery to the brain's blocked vessel using X-ray guidance.
- Insert a small stent to capture and remove the blood clot.
- Remove the catheter from the groin.
- Apply pressure to stop bleeding and ensure the patient lies flat for 8-12 hours.
- Monitor in the ICU for 24 hours before moving to a regular ward if stable.

Enhancing Stroke Treatment with Biplane DSA
The thrombectomy procedure uses Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography (Biplane DSA), which provides 3D images of blood vessels and guides the catheter accurately to the blockage. This technology ensures precise, quick, and safe treatment, improving patient outcomes.
After the procedure, patients undergo physical therapy to restore neurological and physical functions, aiming for the best possible recovery based on individual conditions.
Free Online Consultation
Article of Neurology Center